Advanced Neurosurgical Care for
Aneurysms, AVMs & Stroke
Comprehensive diagnosis and advanced treatment of complex cerebrovascular disorders, focused on safety and neurological recovery.
Conditions Treated.
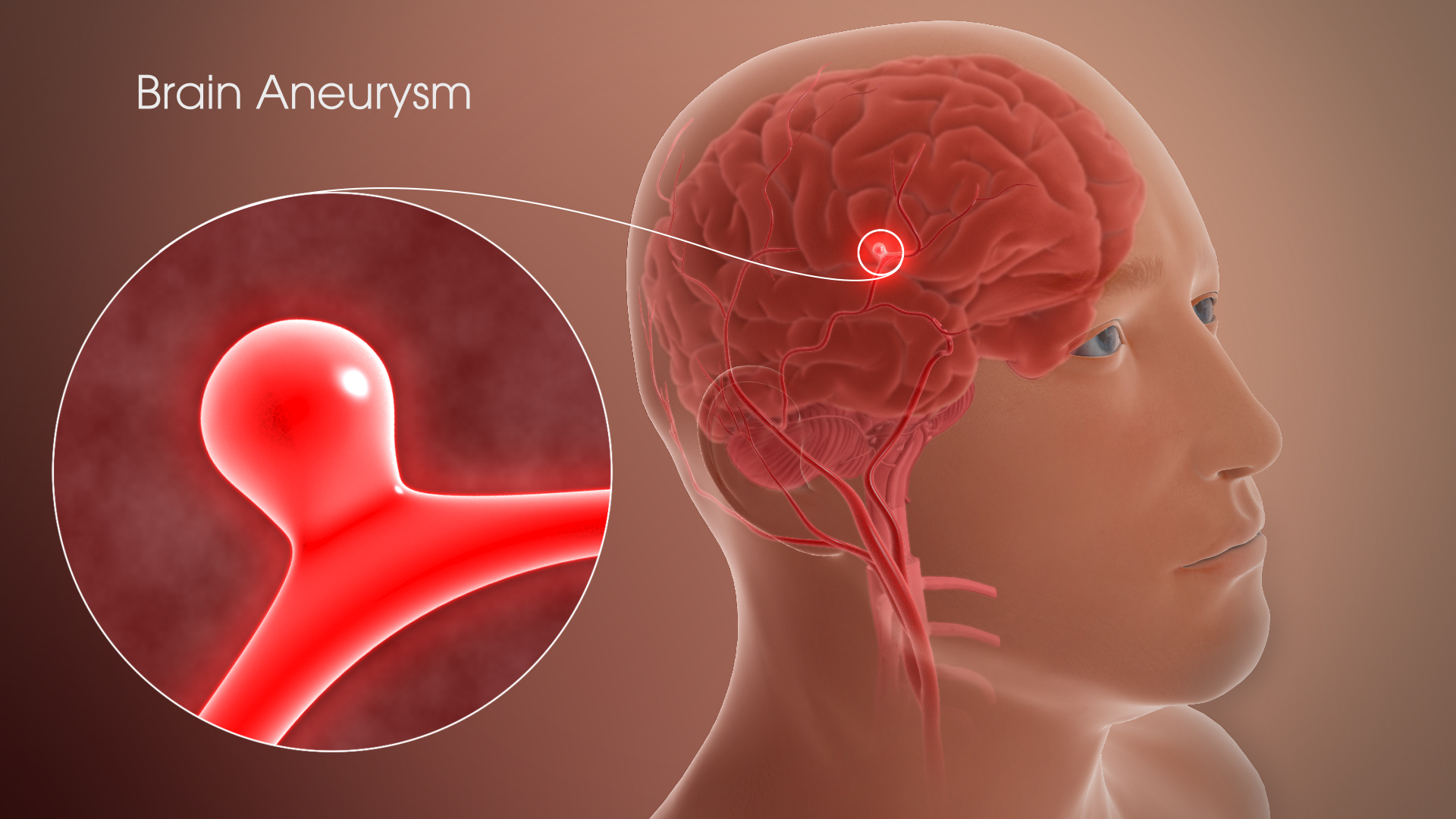
Brain Aneurysms
Aneurysm is a bulge or ballooning of a weak part of the wall of blood vessels inside the brain. It can lead to life-threatening bleed within the brain. 40% of people suffering an aneurysmal bleed die. Only 30% patients make a good recovery. In our country, only 10-20% of aneurysms are detected before rupture. (mostly owing to the fact that we don't have routine screening programs for aneurysms). There are two treatment options for aneurysms, Surgical clipping or Endovascular coiling. Surgery involves making a small opening in the skull and reaching the aneurysm and closing it off with a metal clip. It is a one of the most challenging surgeries in Neurosurgery. Not all aneurysms are accessible or ideal for surgical clipping. Endovascular Coiling is a procedure in which the aneurysm is approached through a small catheter passed into the vessel through a puncture in the groin. The aneurysm is obliterated by filling it with a coil and preventing chances of bleed/rebleed. Sometimes stents or flow diverters (special stents) are used to help coiling. Certain aneurysms are better treated with coiling while some others are suitable for surgery.
Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs)
Arteriovenous malformations (AVM) are abnormal knots or collection of twisted blood vessels where the blood bypasses the normal brain tissue and goes directly from the arterial side (bringing blood into the brain) to the venous side (taking blood back from the brain). Usual symptoms of this condition are seizures, intracranial bleeds, weakness of limbs, speech abnormalities, severe headaches etc. AVMs are extremely difficult conditions to treat. The treatment options include surgical excision of the AVM, endovascular embolization (injecting special glue) to block blood flow through the AVM and Radiation. In many cases, multiple procedures are combined and the treatment is completed in multiple stages.
Stroke & Brain Hemorrhage
Stroke or Infarct happens when blood supply to certain parts of the brain gets cut off due blockage of blood vessels supplying the brain. Usually, this is a condition treated medically or with Mechanical Thrombectomy. Mechanical thrombectomy is a cutting edge technique by which the clot obstructing the blood flow is removed through special catheters and clot retrievers to instantly restore blood flow. If it is done sufficiently early a life-ending or life-altering disease can be defeated and full recovery is possible. In cases where significant areas of brain are already damaged, surgery has a definite role in preventing the dangerous rise of intracranial pressure (pressure inside the skull cavity) and saving the rest of the brain from permanent damage. This surgery entails removing a large part of the skull (bone) to decompress the damaged bulging brain. In cases of recurrent stroke (repeated infarcts), surgery may have a role in augmenting/restoring blood supply to the brain and preventing another stroke. Revascularisation procedures are similar to bypass surgeries done for the heart. It either involves direct revascularisation like bypass (by connecting blood vessels with good flow to areas of the brain with poor blood supply) or indirect revascularisation procedures like Encephalomyodurosynangiosis (using the blood supply of the muscles around the skull to supply the brain). Bypass surgeries are technically demanding and complex but prevent recurrence of strokes.
Treatment Approaches.
Surgical Clipping
Microsurgical placement of a clip to permanently isolate aneurysms.
Endovascular Coiling
Minimally invasive catheter-based treatment using coils and stents.
Mechanical Thrombectomy
Emergency clot removal to restore blood flow in acute stroke.
Decompressive Surgery
Relieves life-threatening pressure caused by brain swelling.
